Plagiarism and Its Consequences
Name: Jheel Barad
Roll No.: 12
Enrollment No.: 4069206420210003
Paper no: 209
Paper code: 22416
Paper name: Research Methodology
Sem.: 4 (Batch 2021- 2023)
Submitted to: Smt S.B. Gardi Department of English, M.K. Bhavnagar University
Introduction:
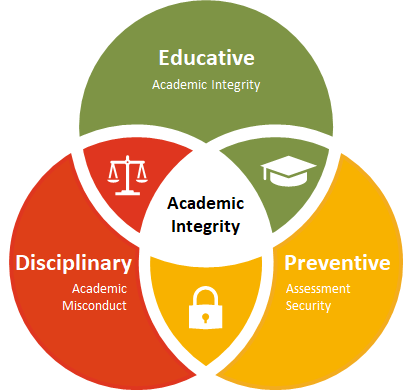
Academic integrity refers to the ethical principles and values that govern academic work and research. It encompasses honesty, fairness, trust, and responsibility in all aspects of academic life, including writing, research, and collaboration. Academic integrity requires students and researchers to be truthful and transparent in their work, to acknowledge the sources of their ideas and information, and to avoid any form of academic misconduct, such as plagiarism or cheating. It also entails upholding the standards of academic excellence and rigor and demonstrating respect for the intellectual property of others. Upholding academic integrity is essential to maintaining the credibility and reputation of academic institutions, and to fostering a culture of trust, fairness, and excellence in academic work.
“Academic integrity is a set of specific practices revolving around independent work, production of original scholarship, accurately and transparently tracing of sources and others’ contributions, and following stated and unstated norms of academic conduct for academic rewards” (Cojocariu and Mareş).
According to Macfarlane et al., there is a relative synonymy between academic integrity and academic honesty. Both concepts encompass similar ethical principles and values, such as honesty, trust, and responsibility in academic work. They also share a common goal of upholding the standards of academic excellence and rigor, while demonstrating respect for the intellectual property of others.
However, academic integrity goes beyond simply avoiding academic misconduct such as cheating on examinations and plagiarism, as identified by Dehn. It also encompasses broader aspects of academic work and research, such as transparent and ethical data collection and analysis, and responsible collaboration with peers and colleagues. Upholding academic integrity is essential not only for the individual's academic success but also for the integrity of academic institutions and the advancement of knowledge and scholarship.
Plagiarism:
Plagiarism is the act of using someone else's work or ideas without giving proper credit or attribution. This can include copying text directly from a source, paraphrasing without citation, or using ideas or concepts from someone else's work without acknowledging their contribution. Plagiarism can occur in academic writing, professional settings, and any other context where ideas or information are being shared. It is considered a serious ethical and academic offense and can lead to consequences such as loss of reputation, legal action, and disciplinary action by academic institutions.
According to the Merriam-Webster online dictionary, "to plagiarize" means:
to steal and pass off (the ideas or words of another) as one's own
to use (another's production) without crediting the source
to commit literary theft
to present a new and original idea or product derived from an existing source
In other words, plagiarism is an act of fraud. (“What is Plagiarism?”)
The word plagiarism is derived from the Latin word ‘plagiorius’, which means "kidnapper" or ‘abductor’. The term ‘plagiarius’ was used in ancient Rome to refer to people who abducted children or slaves and claimed them as their own.
In the 17th century, the term "plagiarism" began to be used in the context of literature and art, to refer to the act of copying or imitating someone else's work without permission or attribution. This usage of the term became more widespread in the 18th and 19th centuries, as literary and artistic works became more valued and copyright laws were established to protect intellectual property.
Forms and Types of Plagiarism:
Plagiarism can take many different forms and can be categorized into various types depending on the extent and nature of the copied content. Some of the common forms and types of plagiarism are:
Forms of Plagiarism:
Repeating or paraphrasing: This form of plagiarism involves repeating or paraphrasing someone else's work without giving proper attribution or citation. This may involve changing a few words or reordering sentences, but the essential idea or argument remains the same.
Taking a particularly apt phrase: This form of plagiarism involves taking a particular phrase, sentence, or expression from a source without acknowledging the original author. This can include idioms, technical terms, or popular expressions.
Paraphrasing an argument or presenting a line of thinking: This form of plagiarism involves paraphrasing an entire argument or presenting a line of thinking that is similar to someone else's work without proper attribution. This can be more difficult to detect than other forms of plagiarism, as it requires a deeper understanding of the original work.
Types of Plagiarism:
Copy and paste: This is the most common type of plagiarism, where a person copies and pastes text from a source without any modifications or acknowledgments. This can occur in written work, online content, and even multimedia presentations.
Disguised plagiarism: This type of plagiarism involves making small changes to the original text, such as replacing words or altering sentence structure, in an attempt to disguise the copied content. However, the essential ideas and arguments remain the same.
Translocation: This involves taking content from one source and placing it in another location without proper attribution or citation. This can occur within the same document or across different documents.
Shake and paste: This form of plagiarism involves taking content from multiple sources and combining it into a single document without proper attribution or citation. This can be more difficult to detect than other forms of plagiarism, as it requires knowledge of multiple sources.
Structural plagiarism: This type of plagiarism involves copying the structure or organization of someone else's work without giving proper credit. This can include copying the outline, headings, or subheadings of a document.
Mosaic plagiarism: This involves copying and pasting content from multiple sources, often in small chunks, and combining them to form a new document without proper attribution or citation.
Metaphor plagiarism: This involves using metaphors or analogies from someone else's work without giving proper attribution or citation. This can be a form of plagiarism when the metaphor or analogy is central to the argument or idea being presented.
Idea plagiarism: This type of plagiarism involves using someone else's idea or concept without proper attribution or citation. This can occur when a person takes an idea from a source and presents it as their own, without acknowledging the original author.
Reasons for Plagiarism
According to Wheeler and Anderson, the battle for intellectual development to become rational can make plagiarism tempting for some students. This suggests that some students may feel pressure to excel academically and may resort to plagiarizing to achieve their goals.
Marshall and Garry also identified various reasons for plagiarism, including a lack of academic writing skills, poor language skills, and cultural factors. They also highlight the importance of understanding referencing, as many students may not be able to distinguish normal citation practices when copying and quoting words, leading to unintentional plagiarism.
Marshall and Garry state, Plagiarism may be caused by less understanding in referencing which a high number of students failed to distinguish normal citation practices when copying and quoting the words as well as confusion about using materials from other sources correctly (Marshall and Garry).
Moreover, anxiety to fail and punishments can also contribute to plagiarism, as students may be afraid of the consequences of poor grades or disciplinary action. Marshall and Garry emphasized that students who are unclear about what constitutes plagiarism may struggle to produce original work, leading them to rely on the work of others.
Another reason for plagiarism is the temptation to take shortcuts. As stated by the definition of plagiarism, it can be easier to copy and paste information from online sources than to conduct original research and develop one's own ideas. This can be particularly tempting for students who may be overwhelmed by the workload or lack the necessary academic writing skills to complete the task.
Some of the common reasons for plagiarism include:
Lack of understanding: One of the primary reasons for plagiarism is a lack of understanding of what constitutes plagiarism. Many students may not be aware of the rules and regulations surrounding plagiarism, including proper citation and referencing practices.
Poor language skills: Students who do not have a strong command of the language may find it difficult to express themselves effectively, leading them to rely on the work of others.
Cultural factors: Cultural differences can also contribute to plagiarism, as some cultures may have different views on academic integrity or may not place as much emphasis on original work.
Lack of academic writing skills: Students who lack the necessary academic writing skills may struggle to produce original work, leading them to rely on the work of others.
Anxiety to fail and punishments: The fear of failure and the consequences of poor grades or disciplinary action can also lead students to engage in plagiarism as a means of avoiding these outcomes.
Temptation: Some students may be tempted to plagiarize due to the ease and convenience of copying and pasting information from online sources.
Lack of fluency in expression: Students who struggle to articulate their ideas may turn to plagiarism as a means of avoiding the difficult task of formulating their own arguments and ideas.
Consequences of Plagiarism:
As stated by the Council of Writing Program Administrators, "We believe that plagiarism is morally and ethically wrong and that it is detrimental to the educational process." Therefore, it is essential to avoid plagiarism by properly citing sources and giving credit where it is due. There are various consequences of Plagiarism
Legal Consequences
Plagiarism can have legal consequences, especially when it involves copyright infringement. According to The Balance Careers, "Plagiarism is illegal because it constitutes copyright infringement, which is a violation of the Copyright Act." The legal penalties for copyright infringement can include fines of up to $150,000 per work infringed and imprisonment for up to five years.
Academic Consequences
Plagiarism can also have serious academic consequences. According to Purdue University's Online Writing Lab (OWL), "In the academic world, plagiarism is considered a serious offense because it undermines the integrity of academic work and the credibility of the entire educational system." The consequences of plagiarism in an academic setting can include failing the assignment, failing the course, or even expulsion from the school. In addition, the student's academic reputation may be permanently tarnished.
Professional Consequences
Plagiarism can also have professional consequences. According to a survey conducted by CareerBuilder, "58 percent of employers said they would automatically dismiss an employee who had plagiarized." In addition, plagiarism can damage one's professional reputation and make it difficult to find future employment.
Ethical Consequences
Plagiarism also has ethical consequences. According to the International Center for Academic Integrity (ICAI), "Plagiarism is a breach of academic integrity and ethics." It undermines the values of honesty, fairness, and respect for intellectual property. Plagiarism can also harm the community of scholars, as it undermines the trust and cooperation that is necessary for academic progress.
Here are some of the real-time Consequences
Joseph Biden
Former Vice President Joe Biden has been repeatedly accused of plagiarism over the years, with several instances of him being caught committing this academic offense. In law school, he failed a course after being found to have plagiarized a paper. Later, he admitted to using sections of a published law review article in an article he wrote for the Fordham Law Review, without giving proper attribution. During his 1988 presidential campaign, Biden was forced to withdraw due to allegations of plagiarism in his speeches, which were found to have been lifted from the speeches of other prominent politicians, including the Kennedys, Hubert Humphrey, and Neil Kinnock. These instances of plagiarism not only brought Biden's academic and political careers into question but also highlighted the importance of academic integrity and the consequences of failing to uphold it.
Alex Haley
Alex Haley, the acclaimed writer, and Pulitzer Prize winner, gained worldwide recognition for his book "Roots" which was later adapted into a popular miniseries. However, Haley's success was overshadowed by accusations of plagiarism. Harold Courlander claimed that Haley had taken sections from his book "The African" and incorporated them into "Roots." The allegation led to a lawsuit in 1978, which resulted in Haley acknowledging that he had indeed plagiarized the information. This incident not only tarnished Haley's reputation as a writer but also highlighted the importance of respecting intellectual property and the severe consequences of violating it. It serves as a reminder that plagiarism is a serious offense that can have far-reaching consequences for an individual's career and reputation.
Martin Luther King
Martin Luther King Jr. is known for his powerful speeches and leadership in the civil rights movement. However, allegations of plagiarism have also been attached to his legacy. It has been claimed that in the 1950s, he plagiarized portions of his doctoral thesis at Boston University, as well as some of his speeches. Investigations revealed that some sections of his thesis had been taken from previous student dissertations and the works of Paul Tillich, the subject of his thesis. While the issue of plagiarism in his speeches is more complex, some have argued that using the words of scripture and other preachers is a common practice in preaching. Nevertheless, the allegations surrounding King's academic work are a reminder that even the most respected and admired figures are not immune to the consequences of plagiarism. This controversy highlights the importance of academic integrity and the need for individuals to uphold ethical standards in all their endeavors.
Monica Crowley
Trump national security spokeswoman Monica Crowley to forgo post amid plagiarism charges Monica Crowley, who was appointed by President-elect Donald Trump for a key national security communications job, has decided to relinquish her post amid multiple allegations of plagiarism. Crowley was set to become the senior director of strategic communications at the National Security Council, but after careful reflection, she has chosen not to take up the position. Crowley has faced several accusations of plagiarism, including in her 2012 book, which her publisher has announced it will no longer sell until she addresses the allegations. Furthermore, her Ph.D. dissertation at Columbia University has also been questioned over plagiarism concerns. In a statement, Crowley expressed her appreciation for the opportunity to be a part of President-elect Trump's team but made no mention of the plagiarism charges. The article notes that the charges were initially reported by CNN and Politico. Politico reported that Crowley’s 2000 dissertation contained more than a dozen sections of text that were lifted, with little to no changes, from scholarly works without proper attribution.
The dissertation was titled “Clearer Than Truth: Determining and Preserving Grand Strategy: The Evolution of American Policy Toward the People’s Republic of China Under Truman and Nixon.”
Romanian PM gives up doctorate after years of plagiarism allegations
Romanian Prime Minister Victor Ponta has handed back his doctorate two years after he was first accused of plagiarizing chunks of his law thesis. The article reports on the resignation of Victor Ponta, the Prime Minister of Romania at the time, after weeks of protests in the country following a nightclub fire that killed 63 people. Ponta had been facing increasing pressure to resign due to allegations of corruption and his handling of the aftermath of the fire. The article also details the political situation in Romania at the time, with Ponta's resignation likely to trigger a period of uncertainty and potential political instability.
Avoid Plagiarism
It is crucial to understand how to avoid plagiarism.
Understand what plagiarism is: Plagiarism is not limited to copying and pasting someone else's work. It also includes paraphrasing or summarizing someone else's work without proper citation. It is important to understand what constitutes plagiarism and the consequences of committing it.
Take notes: When conducting research, take careful notes and make sure to record the source of any ideas or quotes. Keep track of all sources used in your research, including books, articles, websites, and interviews. This will help you properly cite your sources later on.
Use quotation marks: If you are using someone else's words, make sure to use quotation marks and cite the source. This includes direct quotes as well as phrases or sentences that are paraphrased or summarized from the original text.
Paraphrase properly: If you are summarizing or paraphrasing someone else's work, make sure to put the information in your own words and cite the source. It is not enough to just change a few words in a sentence and call it paraphrasing.
Use proper citation: When citing sources, use the appropriate citation style. There are different citation styles such as MLA, APA, and Chicago. Make sure to follow the guidelines for the citation style required by your institution.
Use plagiarism detection tools: There are several plagiarism detection tools available online that can help you check your work for plagiarism. These tools compare your work with a vast database of published works to identify any similarities.
Seek help if needed: If you are unsure about how to properly cite sources or avoid plagiarism, seek help from your teacher or a writing center. They can provide guidance and resources to help you avoid plagiarism.
Plagiarism is a serious offense that can have severe consequences. By understanding what constitutes plagiarism and following these tips, you can avoid plagiarism and ensure that your work is original and properly cited.
Conclusion
In conclusion, plagiarism is a serious offense that can have significant consequences for individuals and organizations. It not only undermines the originality and creativity of ideas but also violates the ethical principles of academic and professional integrity. Plagiarism can result in various penalties, including academic suspension, legal action, and damage to one's reputation. Therefore, it is essential to understand the definition and types of plagiarism and learn how to avoid it by using proper citation and referencing techniques. By doing so, we can promote honesty and credibility in our work and contribute to a more ethical and responsible society. Ultimately, avoiding plagiarism is not only a matter of avoiding punishment but also a matter of maintaining our personal and professional integrity.
Works Cited
Cojocariu, Venera-Mihaela, and Gabriel Mareş. “Academic Integrity in the Technology-Driven Education Era.” Mâță, L. (eds) Ethical Use of Information Technology in Higher Education., 2021, pp. 1-16. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-1951-9_1.
Dehn, Richard W. “Is Technology Contributing to Academic Dishonesty?” Journal of Physician Assistant Education, vol. 14, no. 3, 2003, pp. 190-192.
Gibaldi, Joseph. MLA Handbook for Writers of Research Papers. Modern Language Association of America, 2009.
Gordon, Larry. “Plagiarism Issue Raised in College Work of Dr. King.” Los Angeles Times, 10 November 1990, https://www.latimes.com/archives/la-xpm-1990-11-10-mn-3727-story.html
MAGDALIA. “Alex Haley – Plagiarism.” Sites at Penn State, 22 March 2018, https://sites.psu.edu/magdaliapassionblog/2018/03/22/alex-haley/
Marinas, Radu. “Romanian PM gives up doctorate after years of plagiarism allegations.” Reuters, 16 December 2014,
https://www.reuters.com/article/us-romania-ponta-idUSKBN0JU1N520141216
Marshall, Dr Stephen, and Dr Maryanne Garry. “How well do students really understand plagiarism?” ASCILITE 2005 - The Australasian Society for Computers in Learning in Tertiary Education, 2005, pp. 457-467, https://ascilite.org/conferences/brisbane05/blogs/proceedings/52_Marshall.pdf.
“Plagiarism Definition & Meaning.” Merriam-Webster, 17 February 2023, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/plagiarism?src=search-dict-box#little-gems .
Smith, David. “Neil Kinnock on Biden's plagiarism 'scandal' and why he deserves to win: 'Joe's an honest guy.'” The Guardian, 7 September 2020,
https://www.theguardian.com/us-news/2020/sep/07/neil-kinnock-joe-biden-1987-scandal .
Wagner, John. “Trump national security spokeswoman Monica Crowley to forgo post amid plagiarism charges.” The Washington Post, 16 January 2017, https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/post-politics/wp/2017/01/16/trump-national-security-spokeswoman-monica-crowley-to-forgo-post-amid-plagiarism-charges/
“What is Plagiarism?” Plagiarism.org, 18 May 2017, https://www.plagiarism.org/article/what-is-plagiarism.






No comments:
Post a Comment